Product
[Product name] Medical Glue
[Main ingredients] α-n-Butyl Cyanoacrylate, α-n-Octyl Cyanoacrylate
[Structural formula]
CN
∣
CH2=C–COOC4H9
CN
∣
CH2=C–COOC8H17
[Composition]
Ingredient name | Component proportion |
α-N-butyl cyanoacrylate (NBCA) | 20% |
α-N-octyl cyanoacrylate (NOCA) | 80% |
[Description] This product is a colorless or faint yellow transparent liquid.
[Intended purpose] It is used for the closure of surgical incision close to skin surface edge, including closure of puncture site of minimally invasive surgery and the closure of incision after thorough debridement, and cannot be used for the closure of subsurface skin.
[Model] Smear type
[Specification] 0.3 ml/piece, 0.5 ml/piece, 0.8 ml/piece, 1.0 ml/piece, 1.5 ml/piece, 2.0ml/piece.
[Intended user] Medical staff
[Instructions for use]
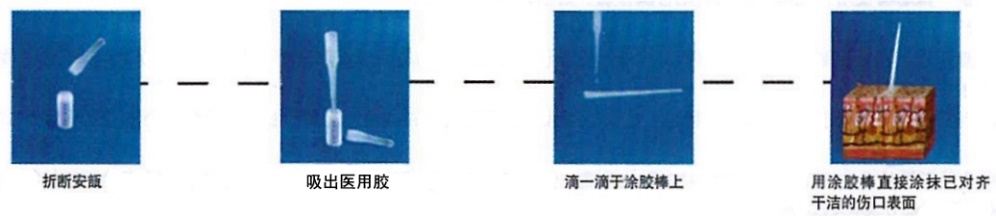
Smear method
1. Take out the glass ampoule filled with medical glue, break it along the mark line, suck out the medical glue from the glue absorbing bottle for later use, thoroughly clean the wound before using the medical glue, and prepare the wound according to surgical norms (i.e., anesthesia, flushing, debridement, hemostasis and closure of deep tissues).
2. Use a dry sterile gauze to wipe the wound, and make the skin surface dry and clean, to ensure that the medical glue can directly contact with tissues for bonding. Moisture can speed up the polymerization of medical glue, and affect the wound closure effect.
3. Drop the medical glue on the broad tip of the glue applicator rod (one drip of glue is about 0.02 ml, and can bond a wound that is 3 cm in length, and if the wound is less than 3 cm, please reduce the amount), directly spray it on the wound or surgical incision (ensure that the skin is free from tension) gently and evenly, to prevent the liquid medical glue from accidentally flowing into improper sites of the body. In addition, it is also required to keep the wound horizontal, and apply the medical glue from the top of the wound.
4. Draw the wound margin with a gloved finger or sterile tweezer. Slowly spray the liquid medical glue on the surface of the closed wound margin in a continuous single layer using a gentle brushing mode. After spraying, draw the wound margin with hands for about 60 s of apposition.
Notes:
The medical glue is polymerized through the exothermic reaction. When spraying, patients may experience discomfort, if the liquid medical glue is applied in larger droplets, rather than being evenly applied. If used in relatively sensitive tissues, such feelings may be stronger. If dropping the medical glue on the broad tip of the glue applicator rod, the discomfort can be significantly alleviated by spraying the medical glue in a continuous single layer as per about 0.02 ml per drip.
Notes:
If the smear tip is applied at the wound margin or the pressure on the surrounding skin is excessive, dehiscence may be incurred at the wound margin, resulting in the entrance of medical glue into the wound. The entering of medical glue into the wound will slow down its healing, and (or) cause a poor appearance after the skin is healed.
Notes:
It is intended to reach the full apposition strength within several minutes after applying the medical glue. After the medical glue is no longer sticky, the medical glue is fully polymerized.
1. The wound closed with the medical glue cannot contact with liquid or ointment drugs or other substances, as these substances can weaken the film formed by polymerization, and cause the separation of skin edges.
2. Wait for a few minutes after the medical glue is used, and use protective dry dressings such as the gauze after it is fully cured/polymerized (not sticky when touching it). Before dressing the bandage, the medical glue should be fully polymerized. The use of dressings, bandages, rubber mats, or tapes before the medical glue is fully polymerized may cause adhesion to the glue film. When removing the dressing, the glue film may be separated from the skin, which will result in the separation from the skin edges.
3. Patients shall be instructed to not remove the polymerized film of the medical glue. The adhesion with skin will break when peeling off the glue film, which will also result in the separation from the skin edges. The medical glue film can be avoided from being peeled off by a patient by covering that dressing on the glue film.
4. For children or other patients who cannot care for the wound properly according to the instructions of doctors, protective dry dressings can be used.
5. The medical professionals shall inform patients that the medical glue generally falls off within 5-10 days, and before that, the therapeutic site shall not be exposed in a wet state for a long term. Patients can gently flush the therapeutic site, but shall avoid rubbing or soaking it. Patients shall be informed of avoiding swimming during the period.
Mechanism of action
The medical glue can rapidly cure into a film under the action of anions (OH- and NH2- in blood or body liquid), and when observing under a scanning electron microscope (SEM), it can be found that the adhesive film and tissue are closely adhered, which can prevent the red blood cells from passing through, promote blood coagulation, and exert the action of closure/hemostasis.
Notification to users
[Indicative instructions]
1. The principle of glue application: debridement, less, uniform, thin and fast.
2. The soft package inside the packaging box includes a non-sterilized area and a sterilized area, and it is especially prompted that, the glue solution in the ampoule in the non-sterilized area adopts sterile filling techniques, and the external wall is not sterilized, so please wipe the external wall with alcohol cotton for disinfection during use.
3. The medical glue shall be used by professional doctors.
[Contraindications]
1. Do not use on active infectious wounds.
2. Avoid using on the surface of mucosa or sites in contact with skin mucosa or skin sites that may frequently contact with body liquid or hair.
3. It is contraindicated in patients with known allergies to cyanoacrylate.
4. Do not use it on subcutaneous tissues.
5. Avoid using at inner organs, vessels, and nervous tissues, and at the conjunctival sac of the eyes.
6. Do not use it on the surface of the eyes.
7. Avoid using on the skin with high tension or at sites with a possible increase in skin tension under large activity such as the hand, elbow or knee, and other joint sites (unless these joints are fixed during the skin healing period, or the skin tension is removed by other wound closure devices, such as the suture or staples), otherwise dehiscence can be incurred.
8. Do not use on a wound that is not covered with skin.
9. This product is contraindicated in patients with known preoperative systemic infections, patients with uncontrolled diabetes, or other diseases or conditions known to interfere with the wound healing process.
[Warnings]
1. This product is for single use only. Please check the sterile package of tools before use, and do not use it if damaged.
2. Do not splash into the eyes, and if the eyes are in contact with the product, use a large amount of normal saline or clean water to wash the eyes. If there is medical glue residue or the adhesion formed by releasing with the eye ointment in the eyes, please ask the ophthalmologist for help. When adhering the facial wound around the eyes with medical glue, adjust the position of patients, to avoid the glue from flowing into the eyes. Patients should close the eyes and protect the eyes with gauze. Apply vaseline around the eyes preventatively, to form a mechanical barrier or retaining dam, which can effectively prevent the glue from accidentally flowing into the eyes of the patient.
3. Keep the product away from children.
4. When spraying, the glue shall not flow below the skin and between the incision tissues, otherwise the wound healing can be influenced.
5. With fast curing speed, the medical glue can bond most human tissues and many other materials, such as surgical gloves and stainless steel. It is required to avoid accidental contact with any human tissues, surfaces of objects and equipment that are not disposable or cannot be easily cleaned with solvents such as acetone. Clear water or alcoholic liquid can speed up the polymerization speed of medical glue. It is not applicable to wet wounds.
6. The medical glue cannot bond the skin pre-coated with vaseline. Therefore, it is required to avoid using vaseline on the skin area to be applied with medical glue for bonding.
7. After the medical glue is used to bond the wound, please notice whether there are any signs of infection. If the wound is found to have any signs of infection, such as redness, swelling, heat, pain and suppuration, it is required to evaluate and treat according to routine treatment of infection.
8. The medical glue should not be applied at sites that are damped and abraded for a long term or repeatedly.
9. The medical glue can only be used after the wound is fully cleaned and debrided according to surgical specification, and if necessary, the anesthetics can be used, to ensure sufficient cleaning and debridement.
10. Do not put the medical glue in any procedure pack or surgical tray that should be sterilized before use. The medical glue will speed up curing when exposed to a hot environment (such as autoclave or ethylene oxide sterilization) or ray (such as gamma ray and electron beam), and lose adhesion properties.
11. One medical glue can only be used for one patient, and after the bonding operation of each wound, it must be discarded and treated as medical waste.
12. Do not re-sterilize the medical glue.
13. After being treated with medical glue, the wound should not contact with other medical solutions or unguents or other substances, as these substances will weaken the polymerized film, and result in dehiscence at skin edges. Thoroughly clean the smear sites to remove any residual local drugs/anesthetics.
14. The medical glue is in a liquid state, and to prevent it from flowing to non-intended areas: ① The wound should be kept horizontal, and sprayed from top to low. ② The medical glue shall be sprayed in a continuous single layer, and shall not be massively sprayed.
15. If intact skin is accidentally bonded together, it is required to remove the medical glue from the skin, without ripping the skin edges apart. Vaseline or acetone can help release the adhesion. Other agents (such as clear water, normal saline, or soapy water) cannot immediately release the adhesion.
16. The medical glue has not been studied regarding the safety and effectiveness of the following wounds:
Wounds, burst stellate wounds, bite wounds caused by animals and humans, and puncture wounds of patients with peripheral angiopathy, insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus, coagulation disorders, or a personal or family history of keloid formation or hypertrophy.
17. The wound can be exposed to sunlight or ultraviolet illumination for a long time after being treated with the medical glue. Their safety and effectiveness on wounds have not been studied.